Industrial Waste Heat
Process Heat Recovery
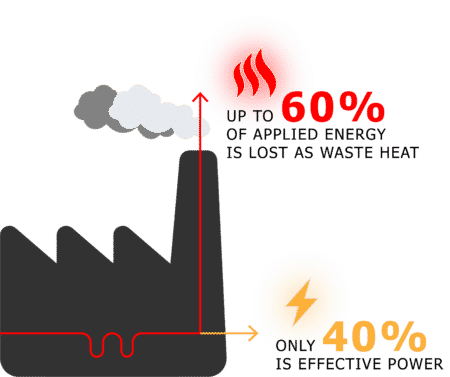
Industrial processes generate tremendous heat. Like most heat generating activities, over half of this heat is vented to the atmosphere or off-loaded into bodies of water. This is the definition of waste heat. In some cases, there are hard infrastructure costs that arise from the effort to get rid of this heat. The costs get even higher when you consider that infrastructure needs to be maintained.
There is often untapped value in the heat that industrial processes create. The heat which is currently wasted presents an opportunity for higher efficiency, lower operating costs, and increased resiliency.
For industries that operate 24/7, the return on investment is even greater. ElectraTherm’s ORC heat recovery units are sturdy enough to run around the clock, alongside any continuous process. That continuous operation runs at maximum efficiency to increase the amount of power produced. This further improves return on investment and strengthens the bottom line. Operators looking to take advantage of their excess heat benefit from increased plant efficiency, reduced energy/fuel costs, and reduced emissions all with one piece of equipment.
ElectraTherm provides a turnkey solution for industrial operations to harness industrial heat sources, lower the temperature of effluent and create clean, on-site electricity all in one process. The solution to convert waste heat into an asset is relatively simple to put in place. Visit our project evaluation form to find out the savings and ROI on ElectraTherm’s waste heat recovery system.

Low Temperature Waste Heat Recovery

It has been estimated that over 90% of industrial waste heat in the United States is at too low of a temperature to economically generate power with traditional heat recovery systems.
ElectraTherm’s next generation, low-temperature waste heat recovery solutions utilize the thermal energy from heat sources as low as 70°C to generate up to 150 kW of emission-free clean energy.
When the waste heat temperatures are lower, heat recovery becomes more difficult. In simple terms, the heat transfer rate is slower than it is with high temps. For most equipment, that puts low temperate heat recovery out of reach.
This is where ElectraTherm excels. ElectraTherm combines the Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC), proprietary technologies and – using hot water as the thermal transfer agent – generates reliable, clean energy. This increases energy efficiency and reduces operating costs.
Waste heat from industrial processes in the United States alone could provide over 10 gigawatts of clean electricity. That’s enough energy to power over 10 million American homes, save industries over $3 billion annually, and create as many as 160,000 jobs.
Industrial Waste Heat Recovery By Industry
Chemical and petrochemical industry
- A large fraction of European industrial energy consumption.
- More than half of the heat is over 400°C.
- Sources include exhaust gases from boilers, heating systems, thermal oxidizers, reactors and flared gas
Paper-and-pulp industry
- Paper mills exhaust air from paper machine dryers.
- Wood refining and grinding processes run at low temps (~70–80°C)
Cement industry
- Exhaust gases from the rotary kiln (~380°C)
- Hot air exiting the clinker cooler (~360°C)
Glass and ceramics industries
- Glass melters, curing ovens (~200°C)
Food and beverages industry
- Variety of temperature levels in the heat consumption (~60°C to 500°C)
- Exhaust gases from boilers, dryers, toast ovens, and fryers (< 200°C)
Nonferrous industry
- Exhaust gases from aluminum melting furnaces (~1,200°C)
- Calcination (refining) process (< 200°C)
- Smelting pots (~400°C)
- Exhaust gases (~200–300°C)
- Melting furnaces (> 850°C)
- Recycling and secondary melting process (> 500°C)
Steel and iron industry
If the global waste heat from steel production were to be converted to clean electricity, over 500 TWh of emission-free power would be produced. The environmental impact – let alone the economic impact – is enormous.
- About 95% of the heat demand lies in the high-temperature range (> 400°C)
- Recovering heat from exhaust gases from boilers (~300°C)
- Exhaust gases from rolling mills (~500°C)
Industrial Heat Exchanger

The standard for any industry that has excess heat is to find a way to get rid of it. Secondary machinery and systems were built for the sole purpose of removing the heat from the machinery, process fluids and the interior space. Until recently, this was seen as best practice. The old way of doing business represents a significant missed opportunity – that is to capitalize on a reliable resource that the business already owns and to reduce or eliminate the cost of discarding what was once thought of as waste.
The Power Module 75 and the Power+ Generator are heat exchangers that take the heat which would normally be discarded, and turn it into useful energy. They have the dual purpose of removing heat from your operation while converting into something useful. It exchanges heat that you don’t need for energy that you do need.
Waste Heat from Industrial Oils, Fluids and Gases
A common application of heat recovery systems is on systems that use thermal fluids as coolant. The coolant picks up heat from machinery and carries it away to keep the machine cool. Such heat is easily recoverable. Such systems can be piped through the ElectraTherm units to capture that heat energy and convert it to electricity. A second application of heat recovery is with those systems that have excessive heat in exhaust gases. These can also be recovered by the ElectraTherm units to take advantage of the value that is being discarded.

Untapped Potential In Waste Heat
Opportunities for taking advantage of industrial waste heat are everywhere. For facilities that generate their own power or use air compressors, boilers, furnaces, kilns, or other heat generating processes – ElectaTherm’s low temperature waste heat recovery may be an excellent fit.
The ElectraTherm units are self-sufficient. Since they generate electricity, they are net positive on an operation’s electricity supply, meaning they generate more electricity than they use. They therefore pay for themselves by providing free electricity after their payback period.
Our project evaluation form can help determine how long that payback period would be.
Typical sectors for industrial waste heat recovery are the metal, paper, glass, ceramic, and chemical industries. If there is access to sufficient hot water then ORC power generation could be within your reach.
Learn more about the benefits that waste heat to power can offer your business.
Questions?
Contact us for a conversation about your unique project needs.
Use our project evaluation form to jump start the estimating process.